Compressed sensing and radio interferometry
Published in 23rd European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), 2015
Abstract
Radio interferometric imaging constitutes a strong ill-posed inverse problem. In addition, the next generation radio telescopes, such as the Low Frequency Array (LOFAR) and the Square Kilometre Array (SKA), come with an additional direction-dependent effects which impacts the image restoration. In the compressed sensing framework, we used the analysis and synthesis formulation of the problem and we solved it using proximal algorithms. A simple version of our method has been implemented within the LOFAR imager and has been validated on simulated and real LOFAR data. It demonstrated its capability to super-resolve radio sources, to provide correct photometry of point sources in a large field of view and image extended emissions with enhanced quality as compared to classical deconvolution methods. One extension of our method is to use the temporal information of the data to build a 2D-1D sparse imager enabling the detection of transient sources.
Hightlights
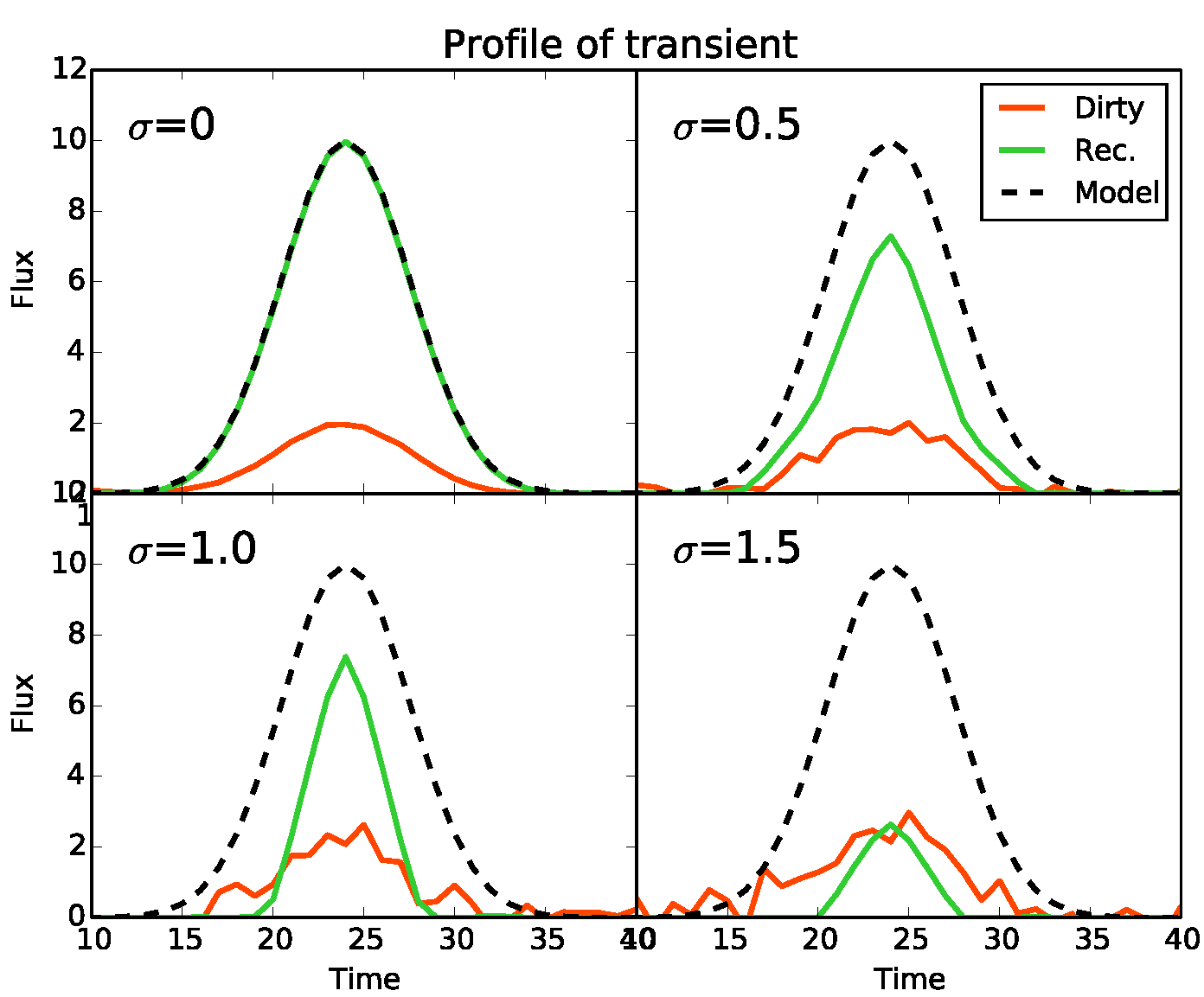
Time profiles at the spatial location of the transient source from the sky model (dash line), the dirty cube (red) and the reconstructed cube (green), for various levels of additive gaussian noise
